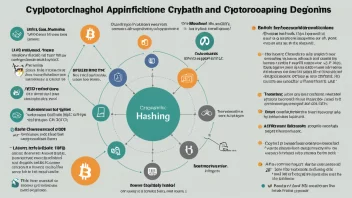
What is a Hash Function?
A hash function is a mathematical algorithm that transforms an input (or 'message') into a fixed-size string of bytes. The output, known as a hash value, is unique to each unique input. Hash functions are widely used in various applications, especially in the realm of cybersecurity.
Why are Hash Functions Important for User Authentication?
Hash functions play a critical role in user authentication systems. They ensure that sensitive information such as passwords is not stored in plaintext, thereby enhancing security. When a user creates an account, their password is hashed before being stored in the database. This means that even if the database is compromised, attackers cannot easily recover the original passwords.
How Do Hash Functions Work in Password Storage?
When a user creates or updates a password, the following steps typically occur:
- The user enters a password.
- The system applies a hash function to the password.
- The resulting hash value is stored in the database.
- When the user attempts to log in, the entered password is hashed again.
- The system compares the newly generated hash with the stored hash to validate the password.
What Makes a Good Hash Function?
A good hash function should have several properties:
- Deterministic: The same input should always produce the same output.
- Quick to compute: It should be easy to compute the hash for any input.
- Pre-image resistance: Given a hash value, it should be computationally infeasible to find the original input.
- Small changes in input result in drastic changes in output: A tiny modification in the input should produce an entirely different hash.
- Collision resistance: It should be hard to find two different inputs that produce the same hash output.
What Are Some Common Hash Functions Used in Authentication?
Several hash functions are commonly used for secure user authentication:
SHA-256: Part of the SHA-2 family, widely used for its strong security features.bcrypt: Designed specifically for password hashing, incorporates a salt to defend against rainbow table attacks.scrypt: Similar to bcrypt, but also requires a large amount of memory, making it resistant to hardware brute-force attacks.Argon2: The winner of the Password Hashing Competition, it is designed to resist both GPU and ASIC attacks.
What Are Salts and Why Are They Used?
A salt is a random value added to the password before hashing. Salts ensure that even if two users have the same password, their hash values will be different. This mitigates the risk of attacks such as rainbow table attacks, where pre-computed hash values are used to crack passwords.
Can Hash Functions Be Broken?
While hash functions are designed to be secure, they are not invulnerable. Advances in computational power and techniques such as brute-force attacks can potentially compromise weaker hash functions. Therefore, it’s crucial to use strong hash functions, along with salts, to enhance security.
Are There Best Practices for Implementing Hash Functions in Authentication?
Absolutely! Here are some best practices:
- Always use a strong hash function designed for password storage, such as bcrypt or Argon2.
- Implement a unique salt for each password before hashing.
- Consider using key stretching techniques to make hashing slower and more resistant to brute-force attacks.
- Regularly update your hashing algorithms to adapt to new security challenges.
Conclusion
Hash functions are a fundamental component of secure user authentication systems. They protect sensitive information by ensuring that passwords are not stored in plaintext and are resilient against various types of attacks. By following best practices and using robust hashing algorithms, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture.