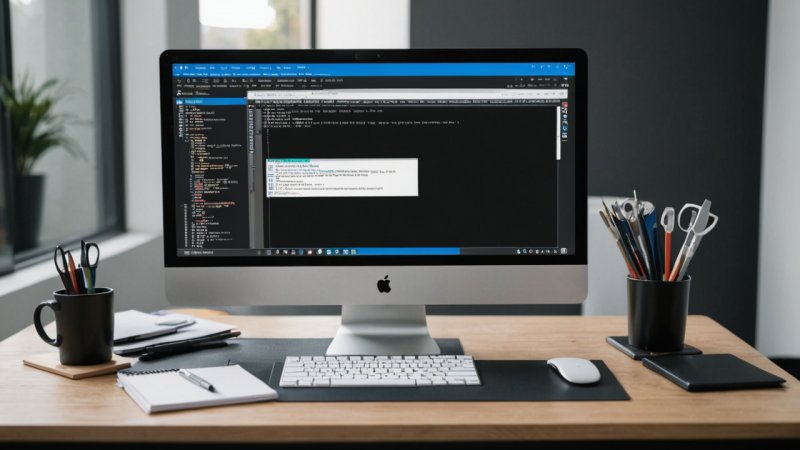
Introduction
In recent years, open source software has transformed numerous aspects of technology, and one of the most significant areas of impact is software testing. This article will explore how open source is redefining the landscape of software testing, the benefits it brings, and how organizations can leverage these tools to enhance their testing processes.
Step 1: Understand the Basics of Software Testing
Before diving into open source tools, it’s essential to grasp the core concepts of software testing. Software testing is a process that evaluates the functionality, performance, and reliability of a software application. It ensures that the software meets the required standards and is free of defects.
- Types of Testing: Unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and acceptance testing.
- Goals of Testing: Identify bugs, improve performance, and ensure user satisfaction.
Step 2: Explore Open Source Testing Tools
There are numerous open source testing tools available that cater to different testing needs. Here are some popular options:
- Selenium: A powerful tool for automating web applications for testing purposes.
- JUnit: A framework for writing and running tests in Java.
- Jest: A delightful JavaScript testing framework with a focus on simplicity.
- Apache JMeter: Used for performance testing and load testing.
Step 3: Implement Open Source Testing Frameworks
To start using open source testing tools effectively, follow these implementation steps:
- Choose the Right Tool: Select a tool based on your project requirements and the technology stack you are using.
- Set Up the Environment: Install the necessary software and dependencies on your local machine or CI/CD pipeline.
- Create Test Cases: Write clear and concise test cases that outline the specific functionality to be tested.
- Run Tests: Execute your test cases using the chosen tool, ensuring to monitor for failures.
- Analyze Results: Review the outputs and logs to identify any issues that need addressing.
Step 4: Integrate Testing into CI/CD Pipeline
Integrating testing into your Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline ensures that tests are run automatically whenever code is updated. To do this:
- Choose a CI/CD Tool: Select tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, or CircleCI that support integration with your testing framework.
- Configure Build Jobs: Set up jobs to execute tests automatically after each build, ensuring that any new code passes all tests.
- Monitor and Report: Implement notifications and dashboards to keep track of test results and failures.
Step 5: Collaborate with the Open Source Community
The open source community is a valuable resource for developers and testers alike. To enhance your testing practices:
- Join Forums and Groups: Engage with other professionals through forums, mailing lists, and social media.
- Contribute to Projects: Share your experiences and improvements to tools, which can help you learn and grow.
- Attend Meetups and Conferences: Participate in events to gain insights and network with experts in the field.
Step 6: Continuous Improvement
Software testing is not a one-time task; it requires ongoing refinement and adaptation. Here’s how to ensure continuous improvement:
- Review and Refine Processes: Regularly assess your testing practices and tools to identify areas for improvement.
- Incorporate Feedback: Gather input from team members and stakeholders to enhance testing effectiveness.
- Stay Updated: Keep track of the latest developments in open source testing tools and methodologies.
Conclusion
Open source software is revolutionizing software testing by providing cost-effective, flexible, and robust tools that enhance the testing process. By understanding the basics, exploring available tools, implementing them effectively, integrating them into CI/CD pipelines, collaborating with the community, and focusing on continuous improvement, organizations can significantly improve their software quality and reliability.
In summary, the steps to leverage open source in software testing include understanding testing fundamentals, exploring relevant tools, implementing frameworks, integrating testing into CI/CD, collaborating with the community, and continuously improving your processes. Embracing these practices will not only enhance your testing but also contribute to the larger open source ecosystem.