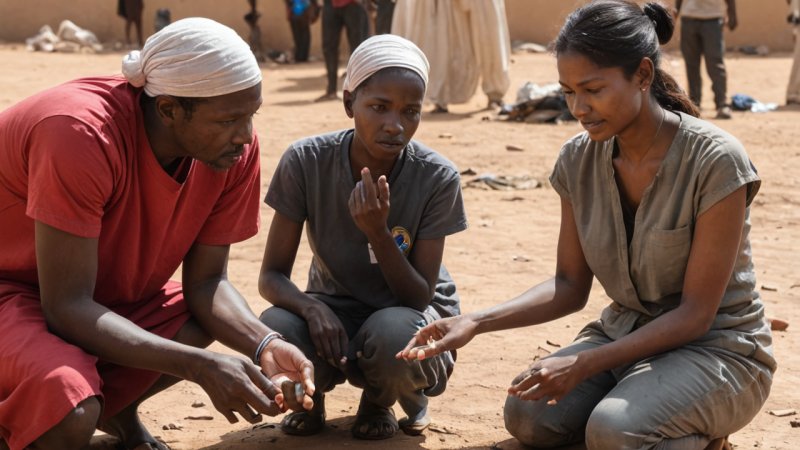
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into humanitarian aid has the potential to revolutionize how we respond to crises, manage resources, and deliver assistance to those in need. However, with great power comes great responsibility. Ethical challenges abound, and it is crucial to navigate these waters carefully to ensure that the benefits of AI are maximized while minimizing harm. Here, we explore some of the most pressing ethical challenges that arise when implementing AI in humanitarian contexts.
Data Privacy and Security
One of the foremost concerns in deploying AI for humanitarian aid is the issue of data privacy and security. Humanitarian organizations often collect sensitive information from vulnerable populations, which can include personal identification details, health data, and location information. This raises significant ethical questions about how this data is stored, used, and protected.
- Organizations must implement robust data protection measures to safeguard personal information.
- Transparency about data usage is essential to maintain trust with the communities being served.
Bias and Fairness in AI Algorithms
AI systems are only as good as the data fed into them. If the training data is biased, the AI can produce unfair outcomes, which can exacerbate existing inequalities in humanitarian aid distribution. This makes it imperative to ensure that AI algorithms are designed to be fair and equitable.
- Regular audits of AI systems can help identify and mitigate biases.
- Involving affected communities in the development process can lead to more equitable AI solutions.
Accountability and Transparency
When AI systems make decisions regarding resource allocation or aid distribution, it can be challenging to determine who is accountable for those decisions. Lack of transparency in AI operations can lead to mistrust and hinder effective humanitarian efforts.
- Establishing clear guidelines for accountability in AI decision-making is crucial.
- Documenting AI processes and decisions can enhance transparency and trust.
Potential for Job Displacement
The introduction of AI technologies in humanitarian aid can lead to concerns about job displacement among local workers. While AI can improve efficiency, it is essential to consider the impact on employment and livelihoods in affected communities.
- Strategies must be developed to upskill workers rather than replace them.
- Engaging local communities in the implementation of AI solutions can create new job opportunities.
Dependency on Technology
Relying heavily on AI technologies may create a dependency that could be detrimental in situations where technology fails or is unavailable. This raises ethical questions about the sustainability of AI-driven solutions in humanitarian contexts.
- Humanitarian organizations should maintain a balance between technology and human intervention.
- Contingency plans must be in place to address technology failures.
In conclusion, while artificial intelligence holds immense potential for improving humanitarian aid efforts, it brings with it a host of ethical challenges that must be addressed. From ensuring data privacy and security to tackling bias in algorithms, organizations must navigate these complexities thoughtfully. By fostering accountability, considering the impact on employment, and balancing technology with human input, we can harness the power of AI responsibly and ethically in the humanitarian sector.