The transition from IPv4 to IPv6 has brought not only an expanded address space but also an array of new protocols designed to enhance network communication. One such protocol is the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP), which plays a crucial role in IPv6 networks. NDP is responsible for several essential functions, including address resolution, router discovery, and network prefix discovery. Understanding NDP and its functionalities is vital for network administrators and engineers as they navigate the complexities of modern networking.
Introduction to IPv6 and NDP
IPv6, or Internet Protocol version 6, was developed to address the limitations of its predecessor, IPv4. With the exponential growth of devices connected to the Internet, IPv4 has struggled with address exhaustion, leading to the development of IPv6, which allows for a vastly larger address space. NDP is one of the key components of IPv6, serving as a replacement for the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) used in IPv4.
What is Neighbor Discovery Protocol?
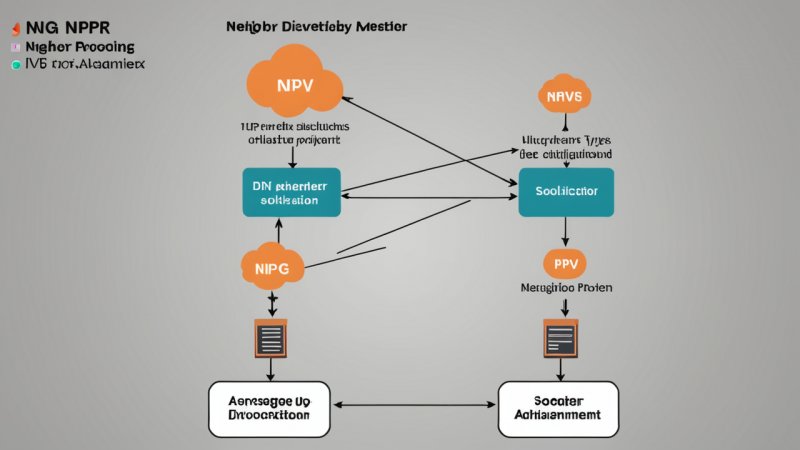
NDP is a set of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMPv6) messages that enable devices on an IPv6 network to discover each other and communicate efficiently. It operates at the link layer and facilitates essential functions such as:
- Address Resolution: NDP enables devices to determine the link-layer address (MAC address) of other devices on the same network segment.
- Router Discovery: NDP allows hosts to discover the routers on the local link and obtain relevant information about them.
- Prefix Discovery: NDP helps hosts to discover the network prefixes used on the link, which is essential for proper address configuration.
- Duplicate Address Detection (DAD): NDP ensures that IPv6 addresses assigned to a device are unique on the local network.
Components of NDP
NDP comprises several message types that facilitate its functionality. These messages include:
Router Solicitation (RS)
Router Solicitation messages are sent by hosts to request the presence of routers on the network. When a host joins a new network, it broadcasts an RS message to find available routers.
Router Advertisement (RA)
In response to RS messages, routers send Router Advertisement messages. These messages contain information such as the network prefixes, the link MTU, and whether the router is a stateful or stateless DHCP server.
Neighbor Solicitation (NS)
Neighbor Solicitation messages are used by a device to determine the link-layer address of a neighbor or to check if a specific IPv6 address is in use.
Neighbor Advertisement (NA)
Neighbor Advertisement messages are sent in response to Neighbor Solicitation messages. They provide the requested link-layer address or confirm the existence of a specific IPv6 address.
Redirect Message
Redirect messages inform hosts of a better route to a destination, guiding them to send their packets to an alternative router.
NDP and Its Functions
NDP performs several critical functions that are integral to the operation of IPv6 networks. Understanding these functions can help network engineers better implement and troubleshoot IPv6 connectivity.
Address Resolution
One of the primary functions of NDP is address resolution. In IPv4, ARP is used to map IP addresses to link-layer addresses (MAC addresses). NDP uses Neighbor Solicitation and Neighbor Advertisement messages to achieve the same goal. When a device needs to communicate with another device on the same local link, it sends out a Neighbor Solicitation message to request the MAC address of the target device. The target device responds with a Neighbor Advertisement message containing its MAC address.
Router Discovery
NDP simplifies the process of router discovery. When a host connects to an IPv6 network, it sends out Router Solicitation messages to identify available routers. Routers on the network respond with Router Advertisement messages, providing information about their capabilities and the network prefixes they manage. This enables hosts to configure their IP addresses and routing information automatically.
Prefix Discovery
Prefix discovery is crucial for hosts to configure their IPv6 addresses correctly. Router Advertisement messages include the prefix information, allowing hosts to create their own IPv6 addresses based on the provided prefixes. This process can be done statelessly, meaning that the host can generate its address without needing a server to assign it.
Duplicate Address Detection
Duplicate Address Detection (DAD) is a mechanism that ensures that no two devices on the same local link use the same IPv6 address. Before a device assigns itself an IPv6 address, it sends a Neighbor Solicitation message to check if that address is already in use. If it receives a Neighbor Advertisement in response, it indicates that the address is taken, and the device must choose a different address.
NDP Security Considerations
While NDP is a powerful protocol, it is not without its security issues. Several attacks can exploit vulnerabilities in NDP, including:
Neighbor Spoofing
In a neighbor spoofing attack, an attacker sends false Neighbor Advertisement messages to convince a host that the attacker’s device is the intended target. This can lead to man-in-the-middle attacks and data interception.
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
An attacker can flood the network with excessive Router Solicitation or Neighbor Solicitation messages, overwhelming routers and causing service disruptions.
Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate these risks, network administrators can implement several strategies:
- Secure Neighbor Discovery (SEND): This protocol adds cryptographic signatures to NDP messages to authenticate the sender and ensure message integrity.
- Filtering and Rate Limiting: Network devices can filter NDP messages based on known device addresses and apply rate limits to mitigate flooding attacks.
- Monitoring and Logging: Continuous monitoring of NDP traffic can help identify unusual patterns indicative of attacks.
Real-World Applications of NDP
NDP is widely utilized in various real-world applications and scenarios, which highlight its importance in modern networking.
Home Networking
In home networks, routers often utilize NDP to facilitate communication between devices. For example, when a new device, such as a smart home appliance, connects to a router, NDP enables the device to discover the router and obtain necessary configuration information.
Enterprise Networks
In enterprise environments, NDP is essential for managing large networks with multiple devices. It allows for dynamic addressing and simplifies the process of adding new devices to the network, enhancing operational efficiency.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The proliferation of IoT devices relies heavily on NDP for communication. As these devices often operate in IPv6 networks, NDP allows them to discover each other and the network infrastructure seamlessly.
Conclusion
The Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) is a fundamental component of IPv6, enabling critical functions such as address resolution, router discovery, and duplicate address detection. While it simplifies networking and enhances device communication, it is essential to acknowledge and address the security vulnerabilities associated with NDP. By implementing appropriate mitigation strategies, network administrators can ensure the reliability and security of their IPv6 networks. Understanding NDP and its applications is vital for professionals navigating the evolving landscape of network protocols.